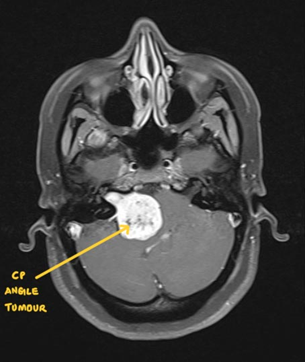
Tumour
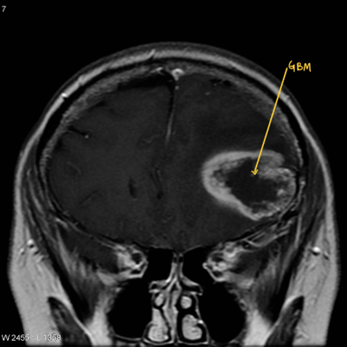
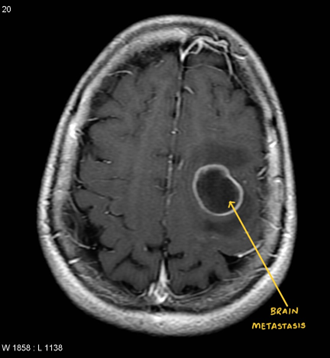
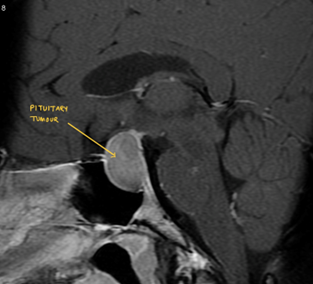
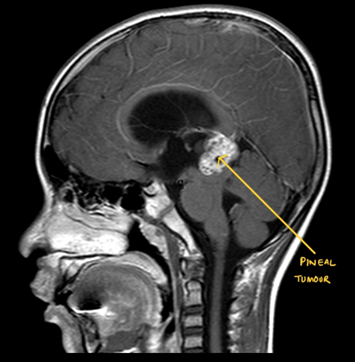
Any space-occupying lesion SOL in the brain is termed a Brain Tumour. Brain tumours can be benign or malignant. To decide brain tumour as benign or malignant Biopsy will be required. Biopsy should be done either by removing the tumour or taking a small part of the tumour for analysis. Surgery can be planned endoscopically or microscopically. Patients with undiagnosed brain tumour/SOL should undergo a biopsy of the tumour as soon as possible. If the tumour comes out to be benign, the patient may not require any surgery in the future. If the tumour comes out to be malignant, the patient will require chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Only after a biopsy, a neuro radiation oncologist can give radiation therapy. The surgery should be planned as earliest as possible after the doctor’s direction to avoid brain damage due to the existing tumour. In certain circumstances, the patient who has a brain tumour may develop a haemorrhage in the side brain tumour or collection of fluid in the brain ( hydrocephalus ). These are the patients who may require surgery in an emergency.
The patient who has a Brain tumour may have symptoms of either of the following. They may present as headaches associated with vomiting/convulsion/paralysis/vision or hearing problems/difficulty in walking/speech problems/face sensation changes/vertigo..etc
It is very necessary for those who have such symptoms should contact to a Neurosurgeon as soon as possible to get evaluated.


0 Comments
* * * Snag Your Free Gift: https://eocenovani.cz/index.php?dmgo06 * * * hs=5160d4c8331713e24180681425392017* ххх*
bjcjni